Lidar

Lidar is an active optical measurement of the distance between ground and the sensor using Laser rays to generate precise terrain and surface models, which also collects data of objects. The precision of the collected data are typically better than 10cm in Z and point densities measured on the ground (1 to 100 pts/sqm) defines the detail of the produced models.
Airborne Lidar sensors operate in different wavelength in the infrared bands (1064nm and 1550nm) for topographic surveys and in the green band (532nm) to map shallow water bathymetry. Furthermore, the transmission power and with this also the requirement on eye safety limiting the applications. Higher Lidar power allows penetration of rain forests, but also requires higher flying altitudes and results in lower point densities.
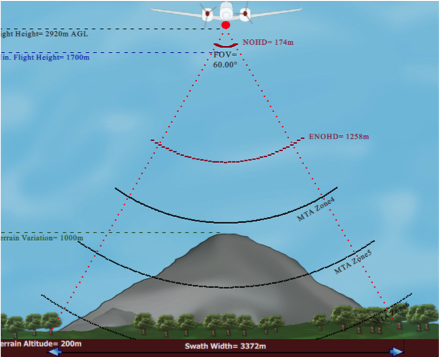
Moreover, there are discrete Lidar sensors (analyzing the returning signal in the air and provide up to 4 returns per Lidar strike) and full waveform Lidar (FWF) systems operational. FWF Lidar sensors are recording the returning signal complete and allowing higher precision of up to 2cm and the detection of more returns per strike, therefore, better use for forestry measurements for instance. Additionally, modern Lidar sensors providing multiple strikes at one time in the air (MTA) allows higher flying altitudes with high scan frequencies, consequently denser scan patterns.
Dimap’s Lidar Suite:
| Lidar sensor | Riegl Q560 | Riegl Q780 | Riegl VQ820 |
| Lidar frequency | 1550nm | 1064nm | 532nm |
| Laser Class | 1 | 3B | 3B |
| Scan Frequency | 240 kHz | 400 kHz | 400 kHz |
| Type of Lidar | Full waveform | Discrete | |
| Scan pattern | Regular cross track | Half circle | |
| Number MTA Zone | 1 | 15 | 5 |
| Accuracy | 20mm | 25mm | |
| Maximum Flying altitude | 1700m | 4000m | 600m |
| Main application | Topographic mapping, forestry surveys, powerline and infrastructure monitoring, geotechnical surveys | Bathymetric and aquatic transition zones, snow and ice surfaces | |
All rights reserved with Dimap, for technical details contact: Holger.Eichstaedt@dimap-spectral.com